1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
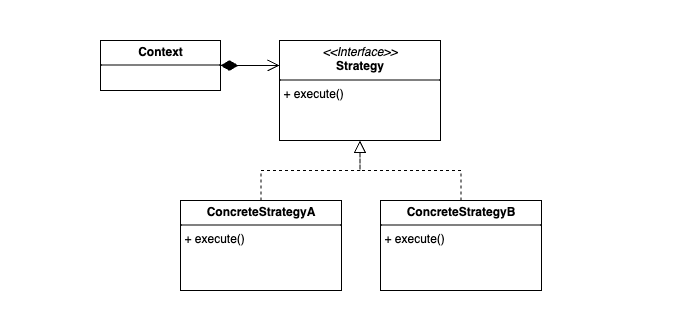
| from konlpy import tag
from typing import Any
from enum import Enum
class TokenizingMethod(Enum):
NOUNS=0
POS=1
MORPHS=2
PHRASES=3
class Tokenizer:
def tokenizing(self, method:TokenizingMethod, input:str | list[str]) -> list[str] | list[list[str]]:
raise NotImplementedError
class TokenizerContext:
def __init__(self, tokenizer:Tokenizer, method:TokenizingMethod):
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.method = method
def set_tokenizer(self, tokenizer:Tokenizer):
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
def set_method(self, method:TokenizingMethod):
self.method = method
def tokenize(self, input: str | list[str]):
return self.tokenizer.tokenizing(self.method, input)
class OktTokenizer(Tokenizer):
def __init__(self):
self.tokenizer = tag.Okt()
self.tokenizing_method = {
TokenizingMethod.NOUNS: self.tokenizer.nouns,
TokenizingMethod.POS: self._wrap_pos,
TokenizingMethod.MORPHS: self.tokenizer.morphs,
TokenizingMethod.PHRASES: self.tokenizer.phrases
}
def _wrap_pos(self, text):
return [word for word, pos in self.tokenizer.pos(text, stem=True) if pos in ["Noun", "Verb", "Adjective"]]
def tokenizing(self, method:TokenizingMethod, input:str | list[str]) -> list[str] | list[list[str]]:
tokenizer_func = self.tokenizing_method[method]
if isinstance(input, str):
result = tokenizer_func(input)
elif isinstance(input, list):
result = [tokenizer_func(text) for text in input]
return result
class KkmaTokenizer(Tokenizer):
def __init__(self):
self.tokenizer = tag.Kkma()
self.tokenizing_method = {
TokenizingMethod.NOUNS: self.tokenizer.nouns,
TokenizingMethod.POS: self._wrap_pos,
TokenizingMethod.MORPHS: self.tokenizer.morphs,
TokenizingMethod.PHRASES: self._not_supported
}
def _wrap_pos(self, text):
return [word for word, pos in self.tokenizer.pos(text) if pos in ["NNG", "NNP", "VV", "VA", "VX"]]
# "NNG" : 일반명사, "NNP" : 고유명사, "VV" : 동사, "VA" : 형용사, "VX" : 보조용언
def _not_supported(self, text):
return NotImplementedError("Kkma does not support phrase extraction")
def tokenizing(self, method:TokenizingMethod, input:str | list[str]) -> list[str] | list[list[str]]:
tokenizer_func = self.tokenizing_method[method]
if isinstance(input, str):
result = tokenizer_func(input)
elif isinstance(input, list):
result = [tokenizer_func(text) for text in input]
return result
class KomoranTokenizer(Tokenizer):
def __init__(self):
self.tokenizer = tag.Komoran()
self.tokenizing_method = {
TokenizingMethod.NOUNS: self.tokenizer.nouns,
TokenizingMethod.POS: self._wrap_pos,
TokenizingMethod.MORPHS: self.tokenizer.morphs,
TokenizingMethod.PHRASES: self._not_supported
}
def _wrap_pos(self, text):
return [word for word, pos in self.tokenizer.pos(text) if pos in ["NNG", "NNP", "VV", "VA", "VX"]]
# "NNG" : 일반명사, "NNP" : 고유명사, "VV" : 동사, "VA" : 형용사, "VX" : 보조용언
def _not_supported(self, text):
return NotImplementedError("Kkma does not support phrase extraction")
def tokenizing(self, method:TokenizingMethod, input:str | list[str]) -> list[str] | list[list[str]]:
tokenizer_func = self.tokenizing_method[method]
if isinstance(input, str):
result = tokenizer_func(input)
elif isinstance(input, list):
result = [tokenizer_func(text) for text in input]
return result
class HannanumTokenizer(Tokenizer):
def __init__(self):
self.tokenizer = tag.Hannanum()
self.tokenizing_method = {
TokenizingMethod.NOUNS: self.tokenizer.nouns,
TokenizingMethod.POS: self._wrap_pos,
TokenizingMethod.MORPHS: self.tokenizer.morphs,
TokenizingMethod.PHRASES: self._not_supported
}
def _wrap_pos(self, text):
return [word for word, pos in self.tokenizer.pos(text) if pos in ["N", "P"]]
# "N" : 체언, "P" : 용언
def _not_supported(self, text):
return NotImplementedError("Kkma does not support phrase extraction")
def tokenizing(self, method:TokenizingMethod, input:str | list[str]) -> list[str] | list[list[str]]:
tokenizer_func = self.tokenizing_method[method]
if isinstance(input, str):
result = tokenizer_func(input)
elif isinstance(input, list):
result = [tokenizer_func(text) for text in input]
return result
class WhitespaceTokenizer(Tokenizer):
def __init__(self):
self.tokenzer = None
def tokenizing(self, method, input):
if isinstance(input, str):
result = input.split(" ")
elif isinstance(input, list):
result = [text.split(" ") for text in input]
return result
|

Comments